685. Redundant Connection II #
题目 #
In this problem, a rooted tree is a directed graph such that, there is exactly one node (the root) for which all other nodes are descendants of this node, plus every node has exactly one parent, except for the root node which has no parents.
The given input is a directed graph that started as a rooted tree with N nodes (with distinct values 1, 2, …, N), with one additional directed edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to N, and was not an edge that already existed.
The resulting graph is given as a 2D-array of edges. Each element of edges is a pair [u, v] that represents a directed edge connecting nodes u and v, where u is a parent of child v.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a rooted tree of N nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the given 2D-array.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Explanation: The given directed graph will be like this:
1
/ \
v v
2-->3
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [4,1], [1,5]]
Output: [4,1]
Explanation: The given directed graph will be like this:
5 <- 1 -> 2
^ |
| v
4 <- 3
Note:
- The size of the input 2D-array will be between 3 and 1000.
- Every integer represented in the 2D-array will be between 1 and N, where N is the size of the input array.
题目大意 #
在本问题中,有根树指满足以下条件的有向图。该树只有一个根节点,所有其他节点都是该根节点的后继。每一个节点只有一个父节点,除了根节点没有父节点。输入一个有向图,该图由一个有着 N 个节点 (节点值不重复1, 2, …, N) 的树及一条附加的边构成。附加的边的两个顶点包含在1到N中间,这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。结果图是一个以边组成的二维数组。 每一个边的元素是一对 [u, v],用以表示有向图中连接顶点 u and v 和顶点的边,其中父节点 u 是子节点 v 的一个父节点。返回一条能删除的边,使得剩下的图是有 N 个节点的有根树。若有多个答案,返回最后出现在给定二维数组的答案。
注意:
- 二维数组大小的在 3 到 1000 范围内。
- 二维数组中的每个整数在 1 到 N 之间,其中 N 是二维数组的大小。
解题思路 #
- 这一题是第 684 题的加强版。第 684 题中的图是无向图,这一题中的图是有向图。
- 这一题的解法也是用并查集,不过需要灵活一点,不要用模板,因为在模板中,存在路径压缩和
rank()优化,这些优化会改变有向边原始的方向。所以并查集只需要记录parent()就够用了。
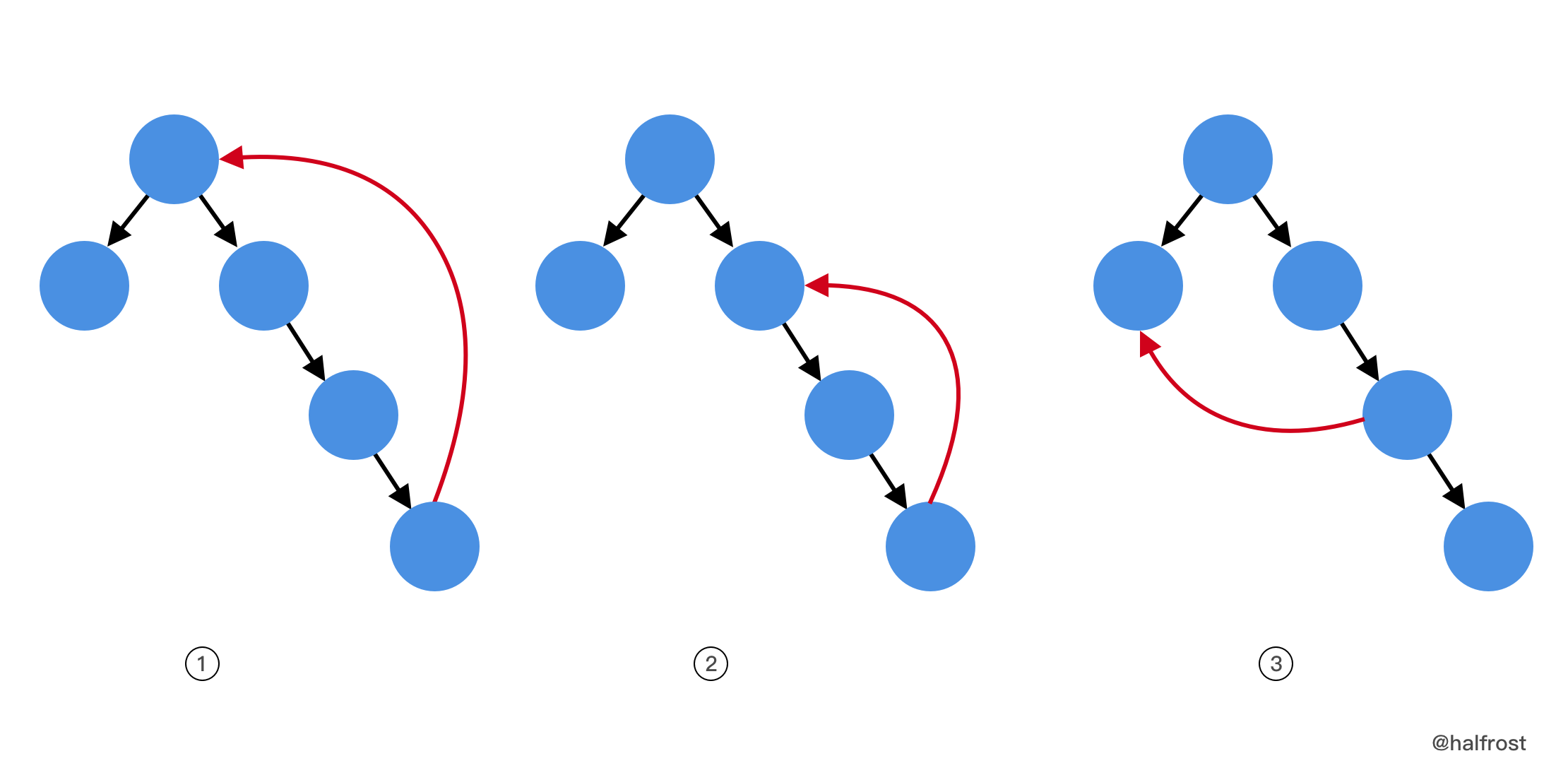
- 经过分析,可以得到上面这 3 种情况,红色的边是我们实际应该删除的。先来看情况 2 和情况 3 。当不断
union()时,加入一条边以后,会使一个节点的入度变成 2,那么记录下这两条边为candidate1和candidate2。将后加入的candidate2这条边先放在一边,继续往下union()。如果candidate2是红色的边,那么合并到最后,也不会出现任何异常,那么candidate2就是红色的边,即找到了要删除的边了。如果合并到最后出现了环的问题了,那说明candidate2是黑色的边,candidate1才是红色的边,那么candidate1是要删除的边。 - 再来看看情况 1。如果一路合并到结束也没有发现出现入度为 2 的情况,那么说明遇到了情况 1 。情况 1 会出现环的情况。题目中说如果要删除边,就删除最后出现的那条边。具体实现见代码注释。
代码 #
package leetcode
func findRedundantDirectedConnection(edges [][]int) []int {
if len(edges) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
parent, candidate1, candidate2 := make([]int, len(edges)+1), []int{}, []int{}
for _, edge := range edges {
if parent[edge[1]] == 0 {
parent[edge[1]] = edge[0]
} else { // 如果一个节点已经有父亲节点了,说明入度已经有 1 了,再来一条边,入度为 2 ,那么跳过新来的这条边 candidate2,并记录下和这条边冲突的边 candidate1
candidate1 = append(candidate1, parent[edge[1]])
candidate1 = append(candidate1, edge[1])
candidate2 = append(candidate2, edge[0])
candidate2 = append(candidate2, edge[1])
edge[1] = 0 // 做标记,后面再扫到这条边以后可以直接跳过
}
}
for i := 1; i <= len(edges); i++ {
parent[i] = i
}
for _, edge := range edges {
if edge[1] == 0 { // 跳过 candidate2 这条边
continue
}
u, v := edge[0], edge[1]
pu := findRoot(&parent, u)
if pu == v { // 发现有环
if len(candidate1) == 0 { // 如果没有出现入度为 2 的情况,那么对应情况 1,就删除这条边
return edge
}
return candidate1 // 出现环并且有入度为 2 的情况,说明 candidate1 是答案
}
parent[v] = pu // 没有发现环,继续合并
}
return candidate2 // 当最后什么都没有发生,则 candidate2 是答案
}
func findRoot(parent *[]int, k int) int {
if (*parent)[k] != k {
(*parent)[k] = findRoot(parent, (*parent)[k])
}
return (*parent)[k]
}