1157. Online Majority Element In Subarray #
题目 #
Implementing the class MajorityChecker, which has the following API:
MajorityChecker(int[] arr)constructs an instance of MajorityChecker with the given arrayarr;int query(int left, int right, int threshold)has arguments such that:0 <= left <= right < arr.lengthrepresenting a subarray ofarr;2 * threshold > right - left + 1, ie. the threshold is always a strict majority of the length of the subarray
Each query(...) returns the element in arr[left], arr[left+1], ..., arr[right] that occurs at least threshold times, or -1 if no such element exists.
Example:
MajorityChecker majorityChecker = new MajorityChecker([1,1,2,2,1,1]);
majorityChecker.query(0,5,4); // returns 1
majorityChecker.query(0,3,3); // returns -1
majorityChecker.query(2,3,2); // returns 2
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 200001 <= arr[i] <= 20000- For each query,
0 <= left <= right < len(arr) - For each query,
2 * threshold > right - left + 1 - The number of queries is at most
10000
题目大意 #
实现一个 MajorityChecker 的类,它应该具有下述几个 API:
- MajorityChecker(int[] arr) 会用给定的数组 arr 来构造一个 MajorityChecker 的实例。
- int query(int left, int right, int threshold) 有这么几个参数:
- 0 <= left <= right < arr.length 表示数组 arr 的子数组的长度。
- 2 * threshold > right - left + 1,也就是说阈值 threshold 始终比子序列长度的一半还要大。
每次查询 query(…) 会返回在 arr[left], arr[left+1], …, arr[right] 中至少出现阈值次数 threshold 的元素,如果不存在这样的元素,就返回 -1。
提示:
- 1 <= arr.length <= 20000
- 1 <= arr[i] <= 20000
- 对于每次查询,0 <= left <= right < len(arr)
- 对于每次查询,2 * threshold > right - left + 1
- 查询次数最多为 10000
解题思路 #
设计一个数据结构,能在任意的一个区间内,查找是否存在众数,众数的定义是:该数字出现的次数大于区间的一半。如果存在众数,一定唯一。如果在给定的区间内找不到众数,则输出 -1 。
这一题有一个很显眼的“暗示”,
2 * threshold > right - left + 1,这个条件就是摩尔投票算法的前提条件。摩尔投票的思想可以见第 169 题。这一题又要在区间内查询,所以选用线段树这个数据结构来实现。经过分析,可以确定此题的解题思路,摩尔投票 + 线段树。摩尔投票的思想是用两个变量,candidate 和 count,用来记录待被投票投出去的元素,和候选人累积没被投出去的轮数。如果候选人累积没有被投出去的轮数越多,那么最终成为众数的可能越大。从左往右扫描整个数组,先去第一个元素为 candidate,如果遇到相同的元素就累加轮数,如果遇到不同的元素,就把 candidate 和不同的元素一起投出去。当轮数变成 0 了,再选下一个元素作为 candidate。从左扫到右,就能找到众数了。那怎么和线段树结合起来呢?
线段树是把一个大的区间拆分成很多个小区间,那么考虑这样一个问题。每个小区间内使用摩尔投票,最终把所有小区间合并起来再用一次摩尔投票,得到的结果和对整个区间使用一次摩尔投票的结果是一样的么?答案是一样的。可以这样想,众数总会在一个区间内被选出来,那么其他区间的摩尔投票都是起“中和”作用的,即两两元素一起出局。这个问题想通以后,说明摩尔投票具有可加的性质。既然满足可加,就可以和线段树结合,因为线段树每个线段就是加起来,最终合并成大区间的。
举个例子,arr = [1,1,2,2,1,1],先构造线段树,如下左图。
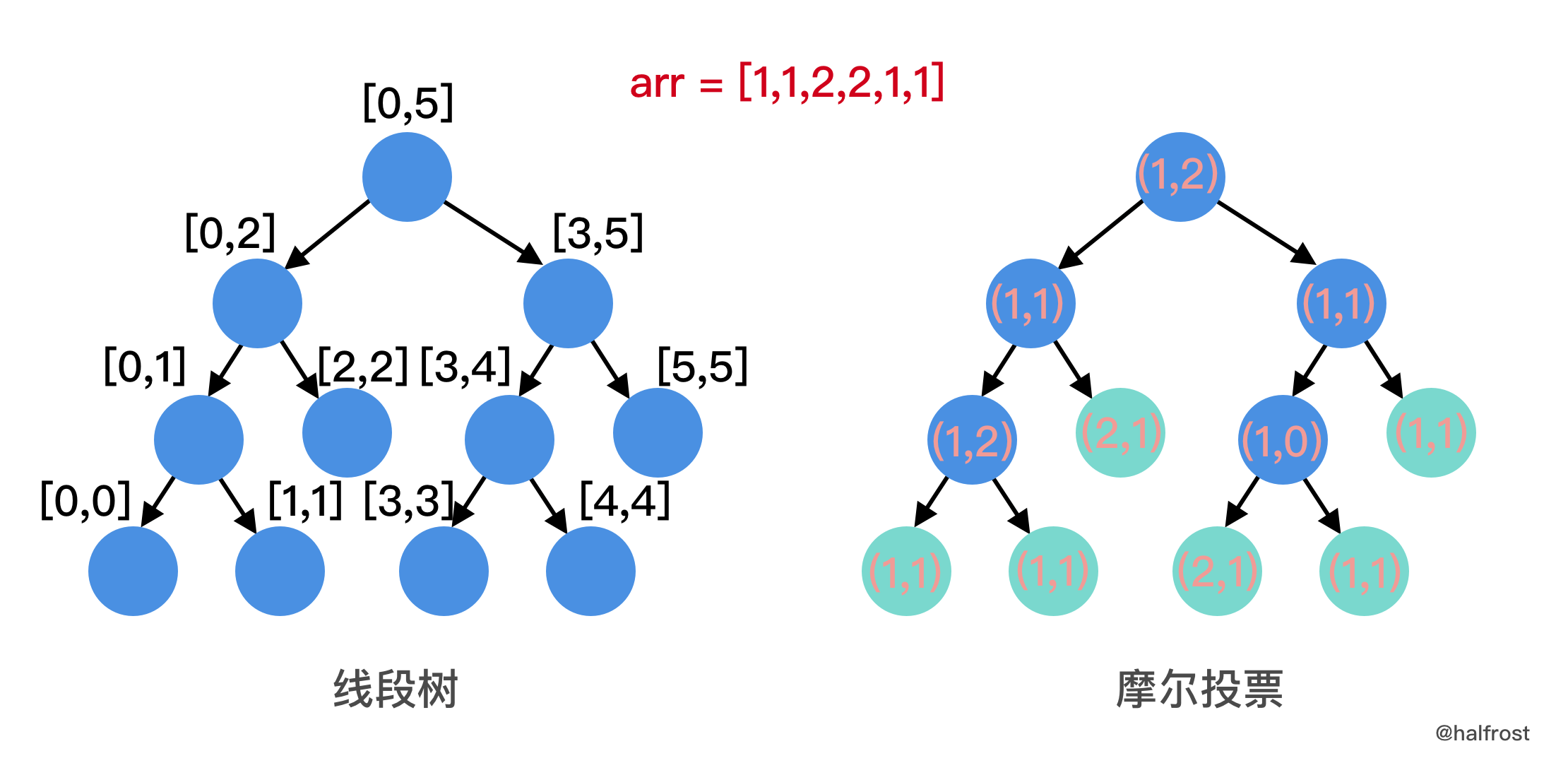
现在每个线段树的节点不是只存一个 int 数字了,而是存 candidate 和 count。每个节点的 candidate 和 count 分别代表的是该区间内摩尔投票的结果。初始化的时候,先把每个叶子都填满,candidate 是自己,count = 1 。即右图绿色节点。然后在 pushUp 的时候,进行摩尔投票:
mc.merge = func(i, j segmentItem) segmentItem { if i.candidate == j.candidate { return segmentItem{candidate: i.candidate, count: i.count + j.count} } if i.count > j.count { return segmentItem{candidate: i.candidate, count: i.count - j.count} } return segmentItem{candidate: j.candidate, count: j.count - i.count} }直到根节点的 candidate 和 count 都填满。注意,这里的 count 并不是元素出现的总次数,而是摩尔投票中坚持没有被投出去的轮数。当线段树构建完成以后,就可以开始查询任意区间内的众数了,candidate 即为众数。接下来还要确定众数是否满足
threshold的条件。用一个字典记录每个元素在数组中出现位置的下标,例如上述这个例子,用 map 记录下标:count = map[1:[0 1 4 5] 2:[2 3]]。由于下标在记录过程中是递增的,所以满足二分查找的条件。利用这个字典就可以查出在任意区间内,指定元素出现的次数。例如这里要查找 1 在 [0,5] 区间内出现的个数,那么利用 2 次二分查找,分别找到
lowerBound和upperBound,在 [lowerBound,upperBound) 区间内,都是元素 1 ,那么区间长度即是该元素重复出现的次数,和threshold比较,如果 ≥threshold说明找到了答案,否则没有找到就输出 -1 。
代码 #
package leetcode
import (
"sort"
)
type segmentItem struct {
candidate int
count int
}
// MajorityChecker define
type MajorityChecker struct {
segmentTree []segmentItem
data []int
merge func(i, j segmentItem) segmentItem
count map[int][]int
}
// Constructor1157 define
func Constructor1157(arr []int) MajorityChecker {
data, tree, mc, count := make([]int, len(arr)), make([]segmentItem, 4*len(arr)), MajorityChecker{}, make(map[int][]int)
// 这个 merge 函数就是摩尔投票算法
mc.merge = func(i, j segmentItem) segmentItem {
if i.candidate == j.candidate {
return segmentItem{candidate: i.candidate, count: i.count + j.count}
}
if i.count > j.count {
return segmentItem{candidate: i.candidate, count: i.count - j.count}
}
return segmentItem{candidate: j.candidate, count: j.count - i.count}
}
for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {
data[i] = arr[i]
}
for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {
if _, ok := count[arr[i]]; !ok {
count[arr[i]] = []int{}
}
count[arr[i]] = append(count[arr[i]], i)
}
mc.data, mc.segmentTree, mc.count = data, tree, count
if len(arr) > 0 {
mc.buildSegmentTree(0, 0, len(arr)-1)
}
return mc
}
func (mc *MajorityChecker) buildSegmentTree(treeIndex, left, right int) {
if left == right {
mc.segmentTree[treeIndex] = segmentItem{candidate: mc.data[left], count: 1}
return
}
leftTreeIndex, rightTreeIndex := mc.leftChild(treeIndex), mc.rightChild(treeIndex)
midTreeIndex := left + (right-left)>>1
mc.buildSegmentTree(leftTreeIndex, left, midTreeIndex)
mc.buildSegmentTree(rightTreeIndex, midTreeIndex+1, right)
mc.segmentTree[treeIndex] = mc.merge(mc.segmentTree[leftTreeIndex], mc.segmentTree[rightTreeIndex])
}
func (mc *MajorityChecker) leftChild(index int) int {
return 2*index + 1
}
func (mc *MajorityChecker) rightChild(index int) int {
return 2*index + 2
}
// Query define
func (mc *MajorityChecker) query(left, right int) segmentItem {
if len(mc.data) > 0 {
return mc.queryInTree(0, 0, len(mc.data)-1, left, right)
}
return segmentItem{candidate: -1, count: -1}
}
func (mc *MajorityChecker) queryInTree(treeIndex, left, right, queryLeft, queryRight int) segmentItem {
midTreeIndex, leftTreeIndex, rightTreeIndex := left+(right-left)>>1, mc.leftChild(treeIndex), mc.rightChild(treeIndex)
if queryLeft <= left && queryRight >= right { // segment completely inside range
return mc.segmentTree[treeIndex]
}
if queryLeft > midTreeIndex {
return mc.queryInTree(rightTreeIndex, midTreeIndex+1, right, queryLeft, queryRight)
} else if queryRight <= midTreeIndex {
return mc.queryInTree(leftTreeIndex, left, midTreeIndex, queryLeft, queryRight)
}
// merge query results
return mc.merge(mc.queryInTree(leftTreeIndex, left, midTreeIndex, queryLeft, midTreeIndex),
mc.queryInTree(rightTreeIndex, midTreeIndex+1, right, midTreeIndex+1, queryRight))
}
// Query define
func (mc *MajorityChecker) Query(left int, right int, threshold int) int {
res := mc.query(left, right)
if _, ok := mc.count[res.candidate]; !ok {
return -1
}
start := sort.Search(len(mc.count[res.candidate]), func(i int) bool { return left <= mc.count[res.candidate][i] })
end := sort.Search(len(mc.count[res.candidate]), func(i int) bool { return right < mc.count[res.candidate][i] }) - 1
if (end - start + 1) >= threshold {
return res.candidate
}
return -1
}
/**
* Your MajorityChecker object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(arr);
* param_1 := obj.Query(left,right,threshold);
*/